Drawing a price floor is simple.
A price floor set above the equilibrium price will.
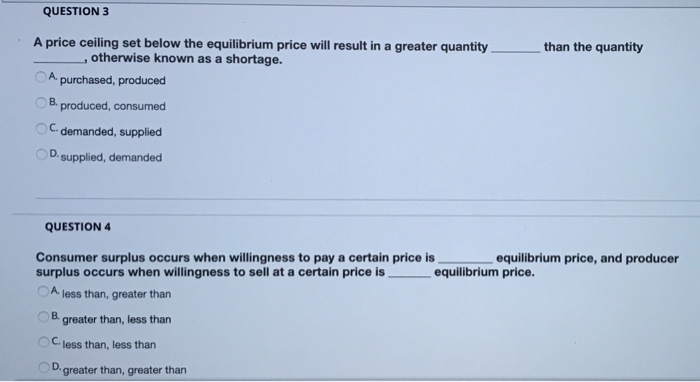
A price ceiling is binding when it is below the equilibrium price.
However price floor has some adverse effects on the market.
When quantity supplied exceeds quantity demanded a surplus exists.
A price floor is a government set price above equilibrium price it is a tax on consumers and a subsidy to producers.
Simply draw a straight horizontal line at the price floor level.
When a price floor is set above the equilibrium price as in this example it is considered a binding price floor.
T f welfare economics is the study of the welfare system.
T f one common example of a price floor is the minimum wage.
How price controls reallocate surplus.
A price floor is a government or group imposed price control or limit on how low a price can be charged for a product good commodity or service.
A price floor example the intersection of demand d and supply s would be at the equilibrium point e0.
The equilibrium price commonly called the market price is the price where economic forces such as supply and demand are balanced and in the absence of external.
The result of the price floor is that the quantity supplied qs exceeds the quantity demanded qd.
For a price floor to be effective it must be set above the equilibrium price.
Rent control and deadweight loss.
It is the legal maximum price so the market wants to reach equilibrium which is above that but can t legally.
Market interventions and deadweight loss.
The intersection of demand d and supply s would be at the equilibrium point e 0.
If price floor is less than market equilibrium price then it has no impact on the economy.
Price floors transfer consumer surplus to producers.
Minimum wage and price floors.
T f a binding minimum wage creates unemployment.
Google classroom facebook twitter.
However a price floor set at pf holds the price above e0 and prevents it from falling.
A price floor example.
If it s not above equilibrium then the market won t sell below equilibrium and the price floor will be irrelevant.
How does quantity demanded react to artificial constraints on price.
Price ceilings and price floors.
However a price floor set at pf holds the price above e 0 and prevents it from falling.
The result is a quantity supplied in excess of the quantity demanded qd.
A price floor must be higher than the equilibrium price in order to be effective.
T f a price floor set above the equilibrium price causes a surplus in the market.
This graph shows a price floor at 3 00.